Search for information
The African Healthcare Market: Opportunities and Challenges Amidst Great PotentialThe African Healthcare Market: Opportunities and Challenges Amidst Great Potential
April 23, 2025, 5:06 pm EDT
The African Healthcare Market: Opportunities and Challenges Amidst Great Potential

Source: Images from the Internet, if there is any infringement, please contact the removal of

Robots and Automated Systems: Ubiquitous Forces in 2045
Robots and Automated Systems: Ubiquitous Forces in 2045more

Taylor Swift and Kanye West's Latest Controversy Ignites Public Outcry
Taylor Swift and Kanye West's Latest Controversy Ignites Public Outcrymore

Yemen's Intangible Cultural Heritage on UNESCO Lists
Yemen's Intangible Cultural Heritage on UNESCO Listsmore
US CDC Plans Large-Scale Study on Vaccine and Autism Link Amid Controversy
US CDC Plans Large-Scale Study on Vaccine and Autism Link Amid Controversymore
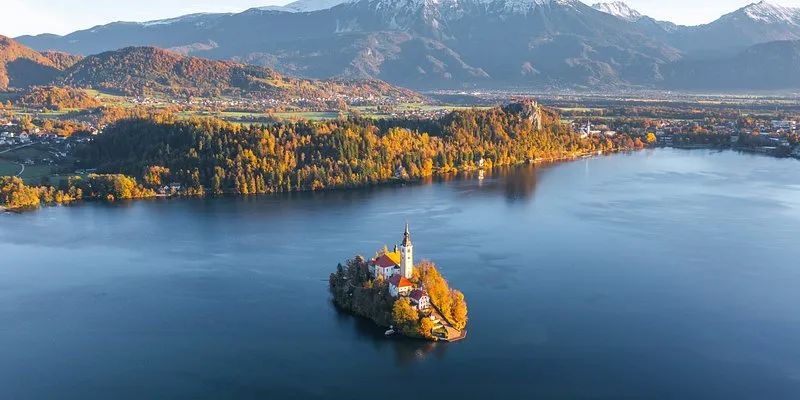

Explore Breathtaking National Parks Around the World
Explore Breathtaking National Parks Around the Worldmore
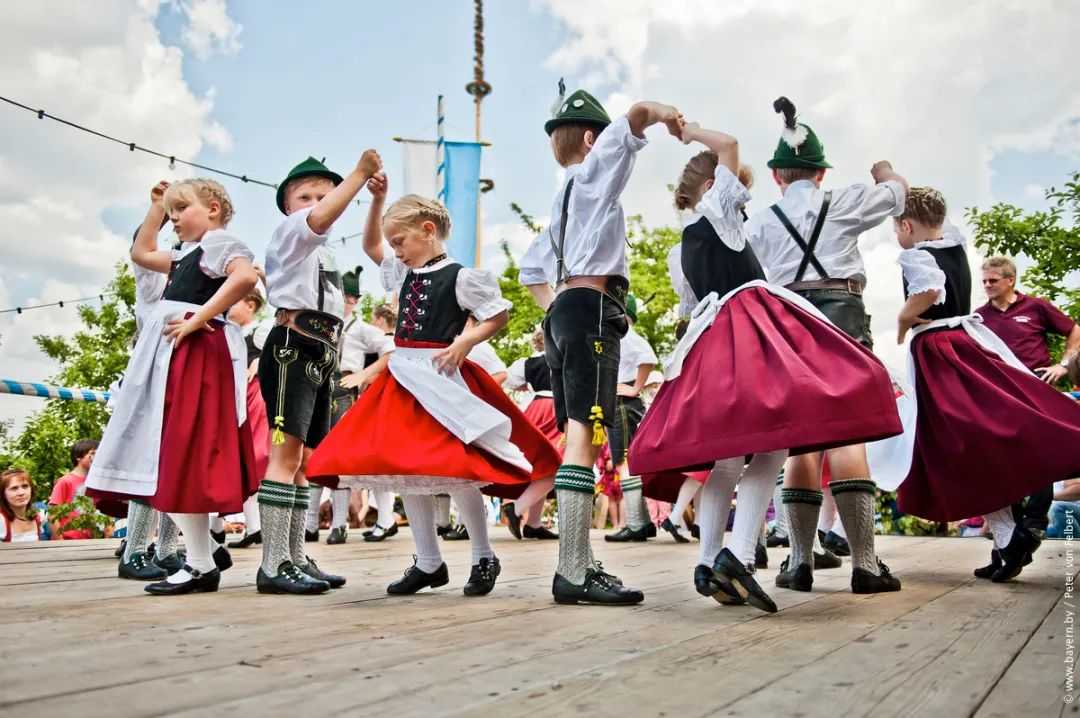

Germany in May: A Month of Festivals and Celebrations
Germany in May: A Month of Festivals and Celebrationsmore
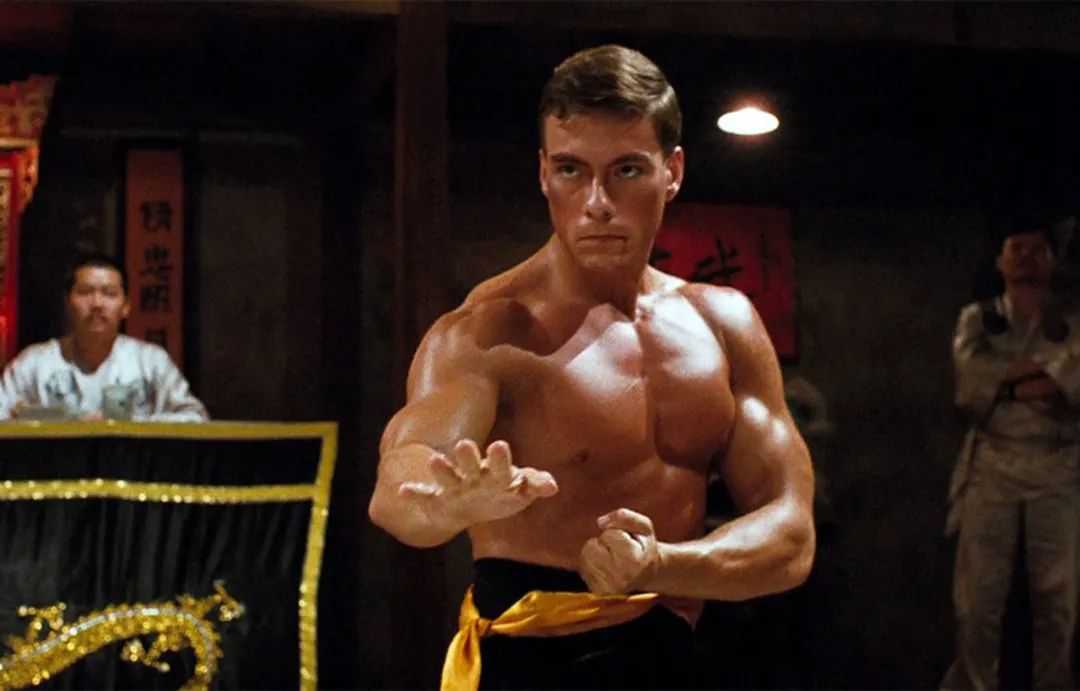

Jean-Claude Van Damme, Hollywood Action Star, Ensnared in Shocking Sex Scandal
Jean-Claude Van Damme, Hollywood Action Star, Ensnared in Shocking Sex Scandalmore
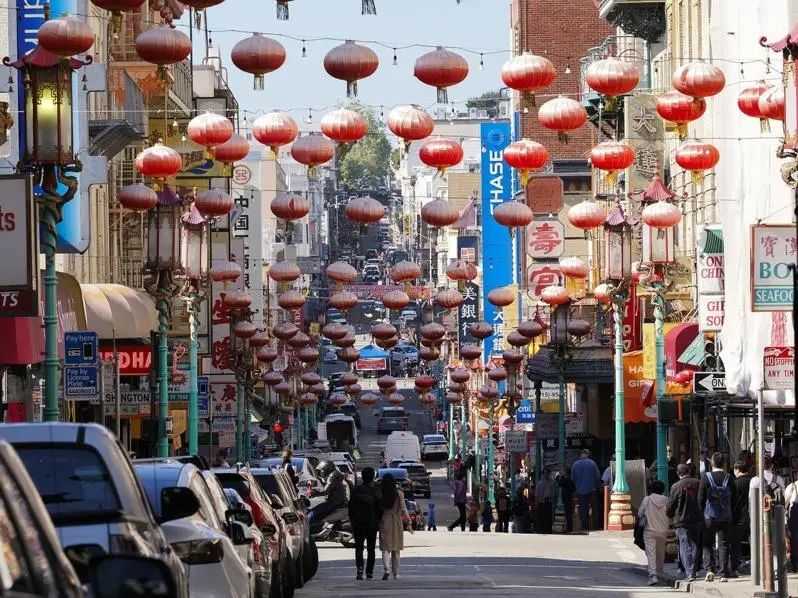

Chinese Restaurants in the US Face Challenges Due to High Tariffs on Chinese Goods
Chinese Restaurants in the US Face Challenges Due to High Tariffs on Chinese Goodsmore

